At the end of 2024, Atom Computing and Microsoft demonstrated the entanglement of large numbers of logical qubits in Atom’s flagship systems, and used them for running algorithms. Since then, the team at Atom has been improving the quality, reliability, and robustness of these logical qubits.
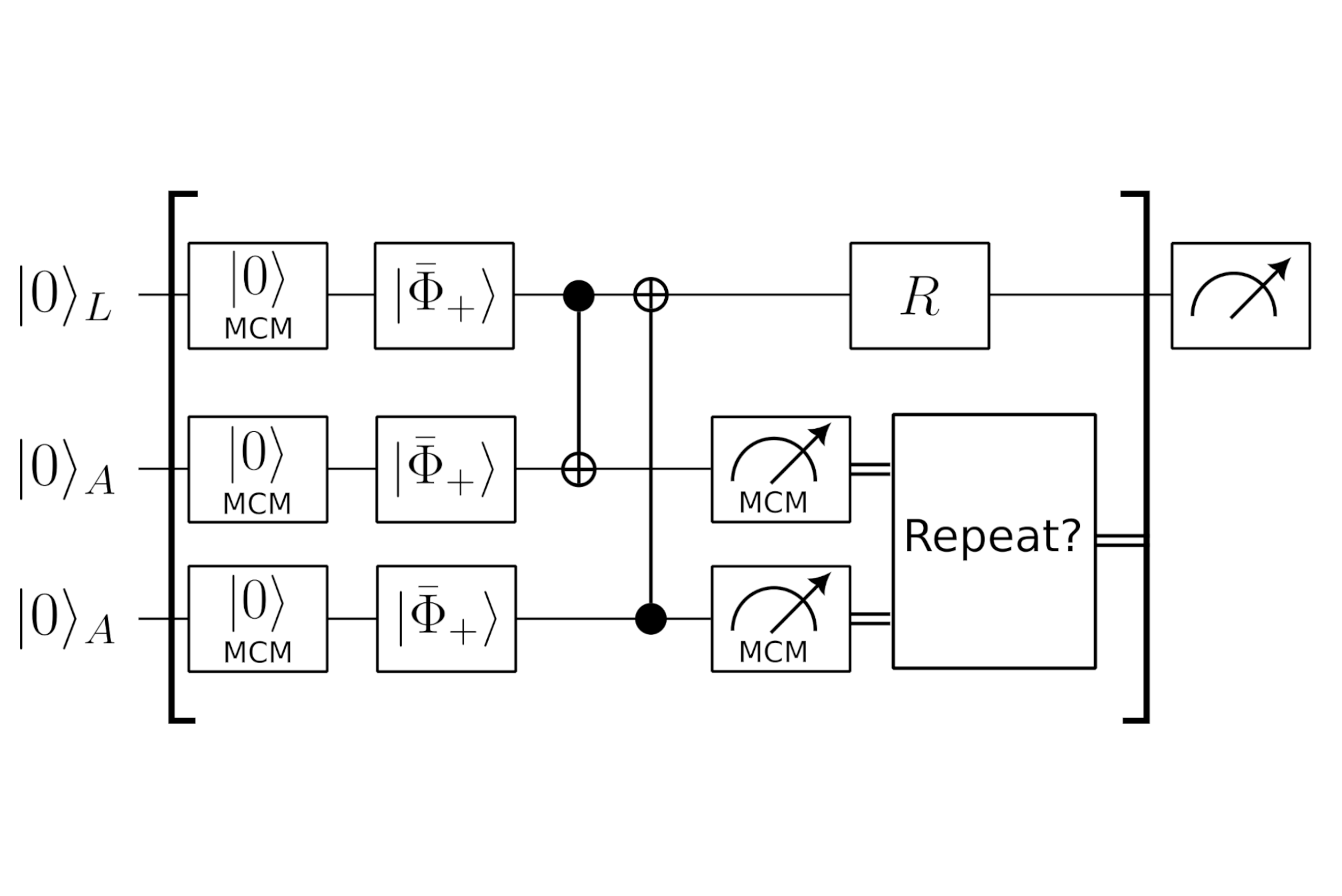
Today, researchers at Atom Computing demonstrated new error correction capabilities which enable high-depth logical circuits on Atom’s neutral-atom quantum processors. Leveraging these capabilities, the team also demonstrated improved system reliability with deterministic creation of logical qubit quantum states (logical Bell pairs) and increased system robustness by replacing qubits that are lost mid-circuit without disrupting the rest of the running algorithm, thereby enabling the platform to run circuits indefinitely.
The key enablers of this progress are an upgraded implementation of Atom’s unique mid-circuit measurement technique (the ability to read out a subset of the qubits in the platform without disturbing all other qubits) with immediate qubit reset and reuse, and the integration of real-time conditional branching (the ability of the system’s software stack to decide what its next operation should be, based on the mid-circuit measurement results).
Atom Computing continues to execute on its roadmap towards fault-tolerant quantum computing, both through advanced research projects and participation in the DARPA QBI program. This progress shows that Atom Computing’s neutral atom technology is not only scalable in the number of logical qubits, but also in their performance. Improvements along both vectors is crucial for being able to build and deliver platforms that can solve large computational problems that enable scientific and economic value beyond classical computing.
Dr. Ben Bloom, Founder and Chief Executive Officer of Atom Computing, said “These demonstrations of our technology continue to prove that Atom is a leading contender to win the race to fault-tolerant quantum computing. With our scalable logical qubits, both in numbers and in quality, we are looking forward to enabling our customers to fully leverage this technology for their researchers and ecosystems.”
The work was supported by researchers from the Microsoft Quantum team.